How do you compare Gigabit switches and 100M switches?
 Dec 28,2023
Dec 28,2023

 Moka
Moka
Gigabit Switches and 100-megabit Switch are two common switch types in the network. They have some obvious differences in data transmission speed, performance, and usage.
Gigabit switch: Supports Gigabit Ethernet, which has a transmission speed of 1 gigabit per second (1 Gbps). This high-speed transmission makes it more suitable for processing large amounts of data and high-bandwidth applications. 100M switch: Supports 100M Ethernet, with a transmission speed of 100 Mbits per second (100 Mbps). Compared with Gigabit switches, the speed is slower and suitable for general home and small business network needs.

Gigabit switch: With higher performance and bandwidth, suitable for handling large-scale data transmission, multimedia streaming, and large network environments. 100M switch: Low performance, suitable for general office and home networks, but may not be ideal for scenarios with large amounts of data transmission and high-performance requirements.
Gigabit switch: Suitable for environments that require high bandwidth and large-capacity data transmission, such as enterprise-level networks, data centers, and scenarios requiring fast file transfer. 100M switch: Usually used in small offices, home networks, or scenarios that do not require high bandwidth.
Gigabit switches: Typically more expensive than 100M switches because they offer higher performance and transmission speeds. 100M switch: Relatively cheap and suitable for cost-sensitive scenarios.
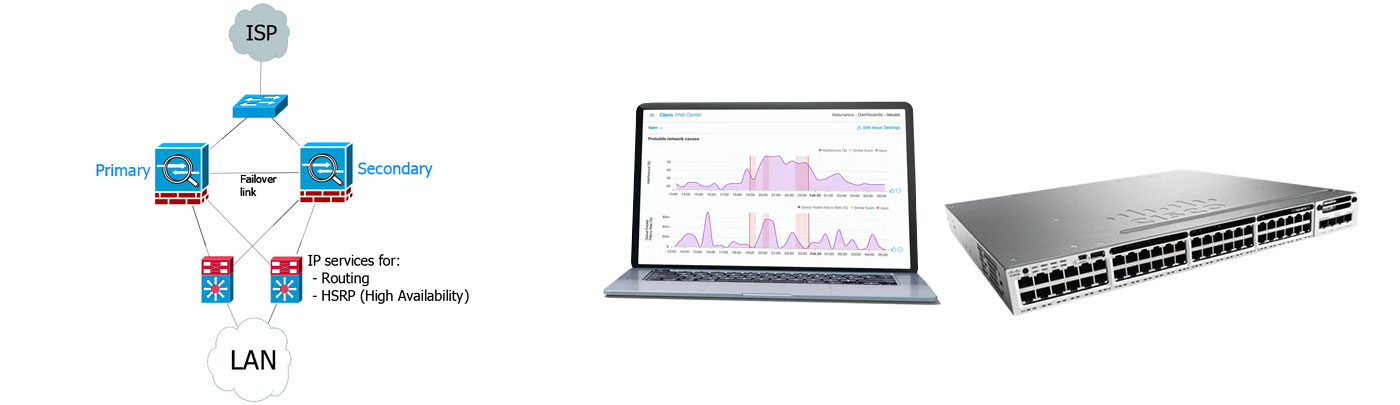
Choosing a Gigabit switch or a 100M switch depends on the network's needs and budget. For large networks and environments with higher performance requirements, Gigabit switches are a more suitable choice. For small networks or limited budget situations, 100M switches may be enough to meet basic needs.





 Home
Home Cisco Catalyst 9300 Series Switches
Cisco Catalyst 9300 Series Switches  You May Also Like
You May Also Like









 Tel
Tel
 Email
Email
 Address
Address












