Link You To Professional Networks

Cisco C1121-4P Risk mitigation with multilevel security,Unified control of wired and wireless networks from a common console for streamlined operations




Cisco ISR 1100 Router C1121-4P Specification
|
Product Code |
C1121-4P |
|
Product Description |
ISR 1100 4P Dual GE SFP Router |
|
Memory (default and maximum) |
DRAM: 4 GB Only C1111X-8P,C1121X-8P,C1126X,C1127X, C1161X models have 8GB DRAM Flash: 4 GB Only C1111X-8P,C1121X-8P,C1126X,C1127X, C1161X models have 8GB Flash |
|
Console |
Micro USB console (Type A). RJ45. |
|
Micro-USB port (reserved) |
Micro-USB port to support remote LTE diagnostics and monitoring tools (Qualcomm CAIT and Spirent UDM) (USB 3.0). |
|
Maximum clients
|
Maximum number of associated wireless clients: 200 per Wi-Fi radio; in total 400 clients per access point. C1109-4PLTEP and C1109-4PLTEW models come with default dual W-ANTM2050D-RPSMA external antenna and all modem have default 8.8 AP autonomous or Mobility Express release. Option to select 8.8 CAPWAP WLC image. |
|
Authentication and security |
AES for Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA2). 802.1X, RADIUS AAA. 802.11r and 802.11i. |
|
Inline PoE |
Optional internal adapter for inline PoE on 4 switch ports for IP phones or external wireless access points; 802.3af-compliant PoE or 802.3at-compliant PoE+. |
|
USB 3.0 |
USB devices supported: -USB eTokens and USB flash memory Devices USB 3.0 supports to be connected externally. View the USB Device Support Data Sheet |
|
Standard safety certifications |
UL 60950-1.and EN 60950-1. CAN/CSA C22.2 No. 60950-1. CB to IEC 60950-1, 2 nd edition with all group differences and national deviations. |
|
EMC emissions |
EN55022/CISPR22, CFR 47 Part 15, ICES003, VCCI-V-3, AS/NZS CISPR22, CNS13438, EN300-386, EN61000-3-2, EN61000-3-3, and EN61000-6-1. |
|
EMC immunity |
EN55024/CISPR24, (EN61000-4-2, EN61000-4-3, EN61000-4-4, EN61000-4-5, EN61000-4-6, EN61000-4-11), and EN300-386. |
|
Radio immunity |
EN301 489-1, EN 301 489-7, and EN301 489-24. |
|
Cellular radio |
EN 301 908-1, EN 301 908-2, EN 301 511, 47 CFR Part 22, 47 CFR Part 24, and EN 301 908-13. |
Cisco Software Defined WAN
Cisco SDWAN is a set of intelligent software services that allow you to reliably and securely connect users, devices, and branch office locations across a diverse set of WAN transport links. SDWAN-enabled routers like the ISR 4000 dynamically route traffic across the “best” link based on up-to-the-minute application and network conditions for great application experiences. You get tight control over application performance, bandwidth usage, data privacy, and availability of your WAN links - control that you need as your branches conduct greater volumes of mission-critical business.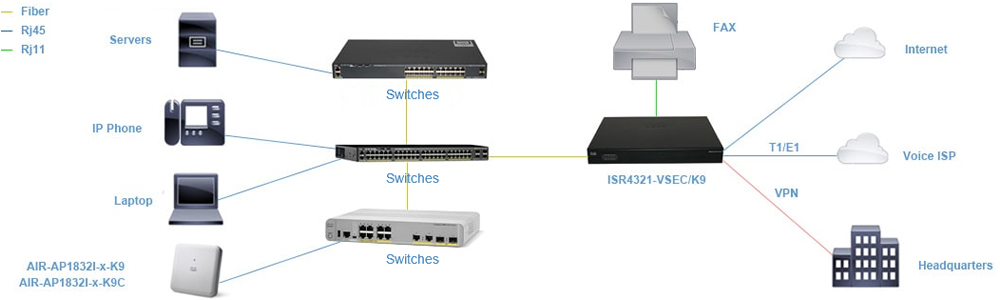
Cisco ISR 11000 Router Cisco C1121-4P Simplicity meets performance

Cisco 1100 Series Integrated Services Routers (ISRs) with Cisco IOS XE Software combine Internet access, comprehensive security, and wireless services (LTE Advanced 3.0 wireless WAN and 802.11ac wireless LAN) in a single, high-performance device. The routers are easy to deploy and manage, with separate data and control plane capabilities.
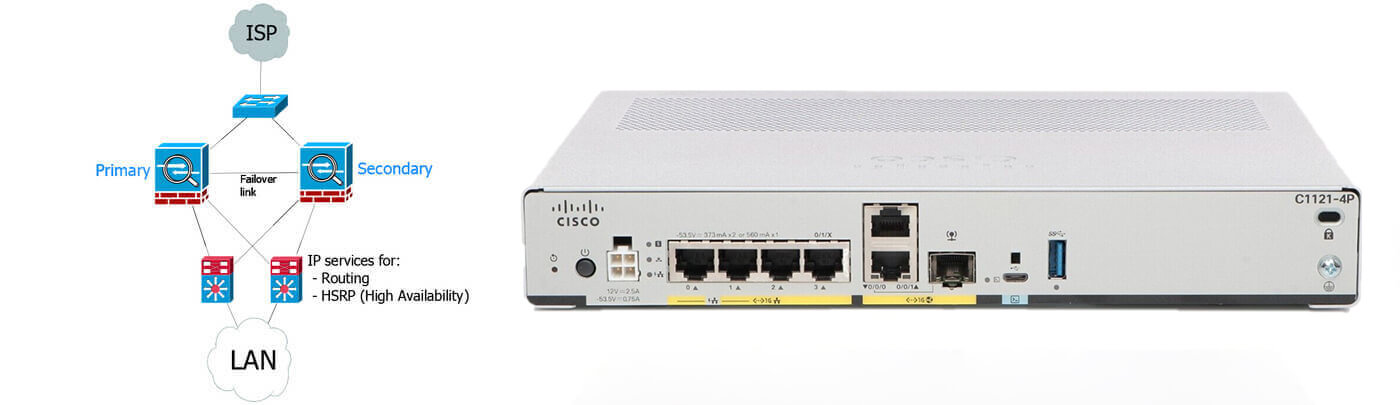

802.11ac Wave 2 with 2x2:2 MIMO technology uses two spatial streams when operating in SU-MIMO or MU-MIMO mode, offering 867-Mbps rates for more capacity and reliability than competing access points.
Flexible deployment through the Mobility Express solution is ideal for small to medium-sized deployments. Easy setup allows the 1000 Series (similar to 1815i) to be deployed on networks without a physical controller.

Cisco 1100 Can be deployed in many different environments where space, heat dissipation, and low power consumption are critical factors (Including Cisco Pluggable smaller form factor technology).






Common steps include checking power supply, confirming network connections, and ensuring up-to-date firmware.
Accessories include additional power adapters, mounting kits, and compatible SFP modules.
Compared to other Cisco routers, the C1121-4P offers balanced performance, security features, and flexibility at a lower cost.
Alternatives include other models in the Cisco 1100 ISR series, providing similar functionality with varying specifications.
Common steps include checking power supply, confirming network connections, and ensuring up-to-date firmware.
